Share this article
The fascinating history of 3D printing
History
3D Printing: A Journey Through Time
Since its humble beginnings in the 1980s, 3D printing has come a long way, completely revolutionizing the way we design and create objects.
The Genesis of SLA 3D Printing by Dr. Kodama
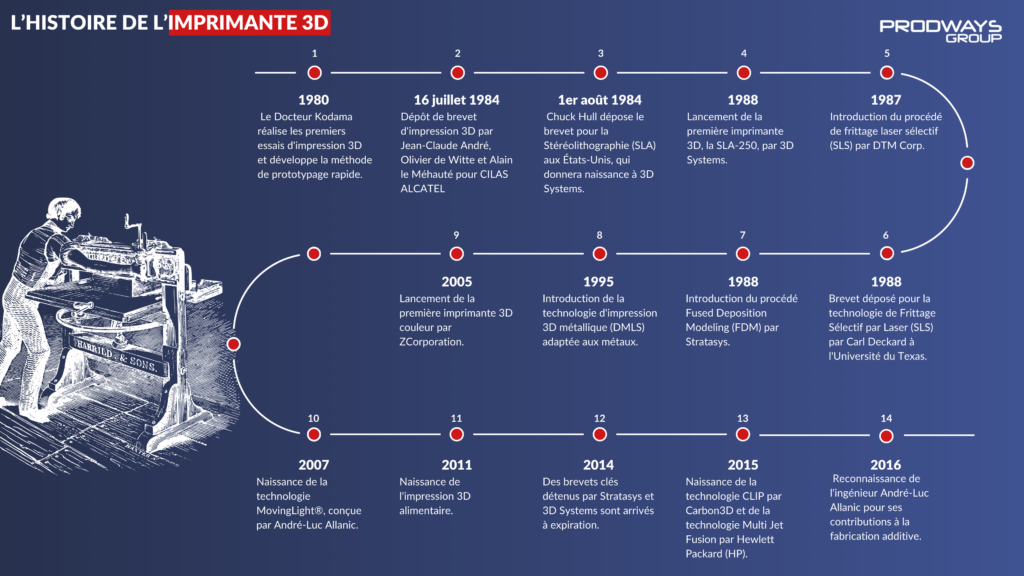
It all began in the 1980s in Japan with the experiments in rapid prototyping by Dr. Hideo Kodama of the Municipal Institute for Industrial Research in Nagoya.
In 1980, he laid the groundwork for what would become 3D printing by developing a new technology to create plastic 3D objects layer by layer, paving the way for Stereolithography (SLA). A photosensitive resin polymerized under the influence of a UV lamp.
However, no patent was filed at that time, and a missed deadline for patent filing prevented it.

The First 3D Printing Patent (1984)
The Emergence of Stereolithography (SLA)
July 16, 1984, marked a significant turning point in the history of 3D printing with the filing of the first 3D printing patent, also known as “additive manufacturing“.
The first patent by CILAS ALCATEL (1984):
These were French researchers, Jean-Claude André, Olivier de Witte, and Alain le Méhauté, who acted on behalf of the company CILAS ALCATEL, a company that would play a crucial role in the early days of 3D printing. This patent paved the way for a technological revolution that would shape the future of design and production. Due to a lack of commercial opportunities, CILAS ALCATEL eventually abandoned this patent.
Chuck Hull and 3D Systems :
A few weeks later, in the United States, Chuck Hull filed a patent for Stereolithography (SLA). This patent would play a key role in the birth of 3D Systems, a company that has since become a giant in the 3D printing industry.

The Emergence of Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS):
In 1987, the company DTM Corp introduced Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). This revolutionary method allows for the manufacturing of objects layer by layer using polymer powders and a laser.
Simultaneously, at the University of Texas, Carl Deckard filed a patent for Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). This technique involves melting powder grains using a laser, thus opening up new possibilities in manufacturing.
The Rise of Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
In 1988, the company Stratasys, founded by Scott Crump, introduced an innovation known as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). This process, based on the deposition of successive layers, would eventually give rise to the household 3D printers we are familiar with today. In less than a decade, the three main 3D printing methods were patented, officially marking the birth of this technology.

Technological Advancements and Innovations
In 1995, the year marked the introduction of Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), a technology similar to SLS but tailored for use with metals. This development expanded the possibilities of 3D printing into the realm of metal manufacturing.
In 2005, ZCorporation revolutionized 3D printing by unveiling the first color 3D printer, which operated on the principle of four-color (quadrichromy) printing. This breakthrough enabled layer-by-layer printing using a material composed of mineral particles bound together by adhesive.
In 2007, the MovingLight® technology was born, created by André-Luc Allanic. This innovation gave rise to some of the most precise and fastest 3D printing machines in the market, pushing the boundaries of accuracy and speed in additive manufacturing.

Diversification and Specialized Applications
Starting from 2011, 3D printing began to expand into new domains, including the realm of food. The American company The Sugar Lab pioneered 3D printing with sugar-based materials.
In 2012, Choc Edge, based in England, introduced the world’s first 3D chocolate printer, marking a delightful innovation in the world of culinary arts and confectionery.

Revolution in Construction
In 2014, China made headlines by announcing the creation of cost-effective houses using 3D printing. This breakthrough generated significant interest in the construction and real estate sectors, paving the way for the design and production of complex structures.
Furthermore, in 2014, key patents held by Stratasys and 3D Systems expired, unlocking the full potential of 3D printing. These patents had constrained the development and accessibility of this technology for years. Their expiration facilitated innovation for other companies, enabling them to create new 3D printing technologies and products without the constraints of patents.
This event marked a major turning point in the 3D printing industry, sparking renewed enthusiasm and a wave of innovation. It led to the development of more affordable and accessible 3D printers, fostering the growth of the maker movement. The adoption of 3D printing also increased across various industries, resulting in a proliferation of 3D-printed prototypes, products, and components. This key moment contributed to democratizing 3D printing technology and sparked an unprecedented period of creativity and experimentation in the years that followed.
Cutting-Edge Technologies (2015)
In 2015, Carbon3D introduced its revolutionary CLIP technology, which enabled 3D printing at a speed seven times faster than traditional methods. Additionally, Hewlett Packard (HP) entered the 3D printing arena with its patented Multi Jet Fusion technology, combining multi-color printing with sintering processes. These developments marked significant advancements in the 3D printing industry, enhancing speed and capabilities for various applications.
Recognition and Conclusion
In 2016, engineer André-Luc Allanic, co-founder of Prodways, was honored with the Engineer of the Year award for his significant contributions to additive manufacturing. Over the past 25 years, he has explored various technologies, leaving an indelible mark on the field.
His work has been instrumental in advancing the capabilities and applications of 3D printing, and his recognition underscores the importance of innovation and expertise in this dynamic and rapidly evolving field.
Discover more
-

Medical
Digital dental workflow Are you up for it?
The integration of digital dental workflow in dental practices represents a major paradigm shift in dentistry. One of the ongoing challenges is the collaboration between dentists and dental laboratories, and the management of impressions, whether they are conventional or digital.
Read more
-

CSR
Our ESG Commitment in 2022: A Year of Notable Achievements
At Prodways Group, we are proud to present a summary of our efforts and achievements in environmental, social, and governance (ESG) responsibility for the year 2022. Our commitment to ESG excellence is at the heart of our corporate strategy, reflecting our determination to operate sustainably and ethically in the 3D printing industry.
Read more
-

History
Additive Manufacturing: Definition, Process, Advantages, and Applications
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, has rapidly become a technological revolution in industrial production.
Read more

